The PC you are using to scrutinize this page uses a CPU to achieve its work. The chip is the center of any normal PC, whether or not it is a work territory machine, a specialist, or a PC. The chip you are utilizing might be a Pentium, a K6, a PowerPC, a Sparc, or any of the various brands and kinds of microprocessors, anyway, they all do around something fundamentally the same as in about a comparable way.
A central processor - in any case, called a CPU or central dealing with the unit - is a completed figuring engine that is made on a singular chip. The necessary microprocessor was the Intel 4004, introduced in 1971. The 4004 was not astounding - all that it could do was incorporate and remove, and it could simply do that 4 pieces at the same time. In any case, tragically everything was on one chip. Going before the 4004, engineers built PCs either from varieties of chips or from discrete portions (semiconductors wired one by one). The 4004 powered one of the principle advantageous electronic small PCs.
A few semiconductors suitably, and you have what's known as a reasoning entryway. Reasoning entryways take two twofold data sources, play out a methodology on them, and return a yield. The OR entryway, for example, returns legitimate if both of the information sources are substantial. The AND entryway checks if the two wellsprings of data are legitimate, XOR checks if only one of the data sources are substantial, and the N-varieties (NOR, NAND, and XNOR) are turned around transformations of their base entrances.
PC memory suggests the region where data and ventures are taken care of. Memory isn't fundamental for the CPU, anyway the CPU should team up personally with it. There are two sorts of PC memory: fundamental, or rule, and discretionary. The CPU relies overwhelmingly upon essential memory for taking care of program headings and the data the rules work on. Guideline memory is temporary in nature and simply holds headings and data for a program while the program is executing. Discretionary memory is the seriously enduring accumulating gave by hard drives and burst drives.
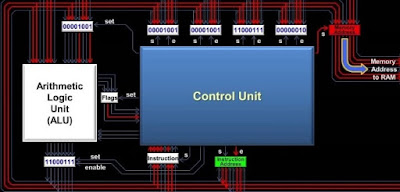
A piece of the CPU known as the control unit is at risk for moving rules and data from discretionary limit into central memory before direction execution. The control unit furthermore moves the delayed consequences of a direction to helper accumulating.
Right when a program runs on a PC, rules are taken care of in PC memory until they're executed. The CPU uses a program counter to bring the accompanying direction from memory, where it's taken care of in a game plan known as get together code. The CPU unwinds the direction into a twofold code that can be executed. At the point when this is done, the CPU does what the direction advises it to, either playing out an action, moving or taking care of data, or changing the program counter to bob to a substitute direction.
Such exercises that regularly can be performed by the CPU consolidate essential mathematical limits like development, derivation, duplication, and division. The CPU can moreover perform relationships between's data objects to conclude whether they're the same. All the staggering things that PCs can do are performed with these several other principal errands. After a direction is executed, the accompanying direction is brought and the cycle continues.